第一列
The main focus of this project is to develop technologies related to silicon-based semiconductor quantum computers, including highly reliable qubits compatible with CMOS processes, cryo-CMOS low-noise, low-power active circuits for controlling and reading qubits, passive circuits designed using IPD (Integrated Passive Device) processes, and integrating qubits with the required active and passive circuits on an IPD substrate to achieve miniaturization. In the future, this can further realize large-scale, universal silicon-based semiconductor quantum computers.
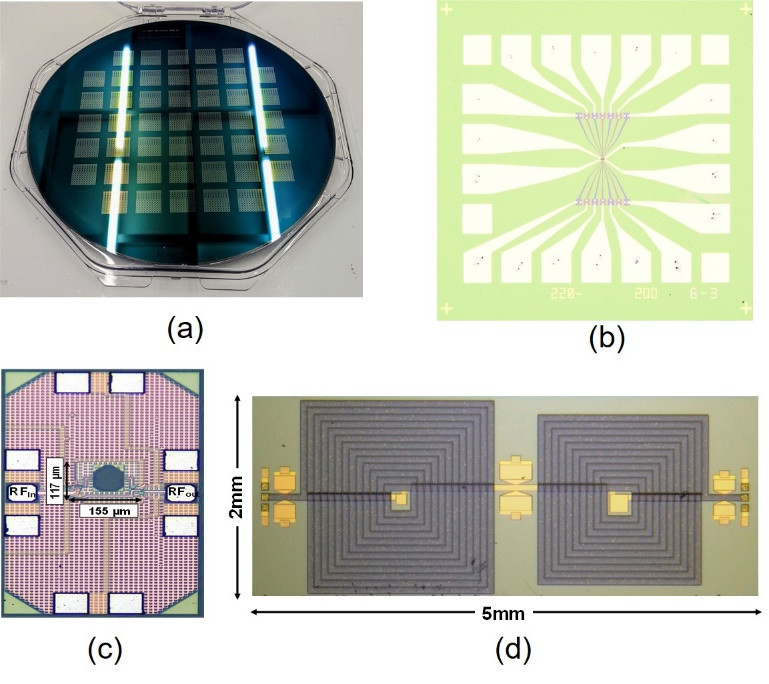
(a) 8" SOI wafer for fabricating silicon-based qubits
(b) Top view of a FinFET qubit
(c) Cryo-CMOS low-noise amplifier
(d) Miniaturized IPD filter
-
Co-PI
-
Chien-Yuan Chang (National Tsing-Hua University)
-
Tzu-kan Hsiao (National Tsing-Hua University)
-
Ta-Chun Cho (Taiwan Semiconductor Research Institute)
Ultracompact Inductorless Noise-Canceling Cryo-CMOS Low-Noise Amplifier for qubit readout
- Problem to be solved:
The RF/microwave low-noise amplifiers are the most important front-end circuit for qubit readout. These amplifiers need to achieve low noise temperature, low power dissipation, and miniaturization specifications. However, current discrete low-noise amplifiers cannot meet these requirements. - Importance/Breakthrough:
We use advanced CMOS processes and propose an inductorless noise-canceling topology for low-noise amplifiers used in qubit readout. Measured results can achieve a noise temperature of 2.2K with a gain of 29dB, and a bandwidth of up to 3GHz. The power consumption is 19.4 mW with a chip area of only 0.018mm2.
This miniaturized amplifier can be integrated with the spin qubits in this project to achieve RF reflectometry qubit readout.
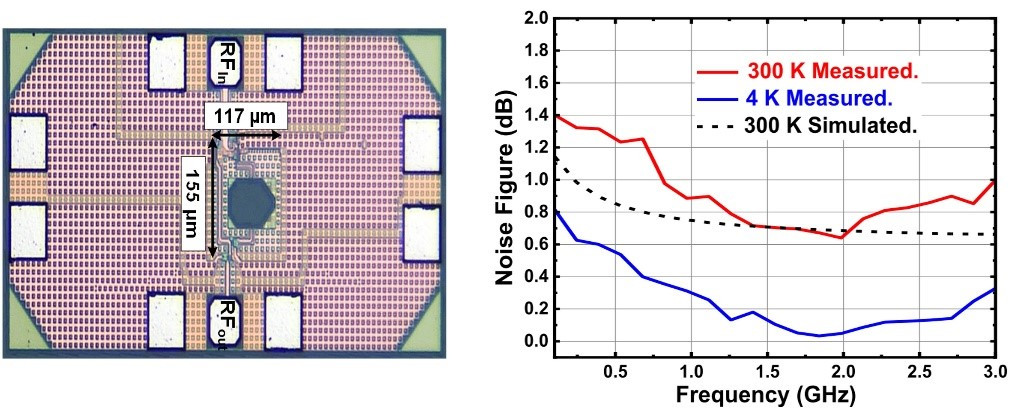
Left: Miniaturized inductorless noise-canceling Cryo-CMOS low-noise amplifier chip photo
Right: Measured and simulated noise characteristics at room temperature and 4K
Reference: M. K. Chaubey, Y. Liu, Y. Chang, P. Wu, H. Tsai, and S. S. H. Hsu*, “Ultracompact inductorless noise-canceling LNAs in 40-nm CMOS achieving 2.2-K noise temperature for qubit readout,” IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Techn., vol. 72, no. 4, pp. 2168-2178, Apr. 2024
