第一列
Quantum computing is in a stage of rapid development. Among available technologies, quantum annealing uses qubits to efficiently solve optimization problems. D-Wave is the world's first provider of quantum annealing computers. As a semiconductor and technology powerhouse, Taiwan is actively investing in the research and development of quantum computing. This project aims to promote the application of D-Wave quantum annealing technology in various research engineering fields and accelerate its practical development. Through planning and deployment, the widespread introduction of the D-Wave platform is expected to promote the research progress and engineering practice of quantum annealing in Taiwan and provide new momentum for industrial development.
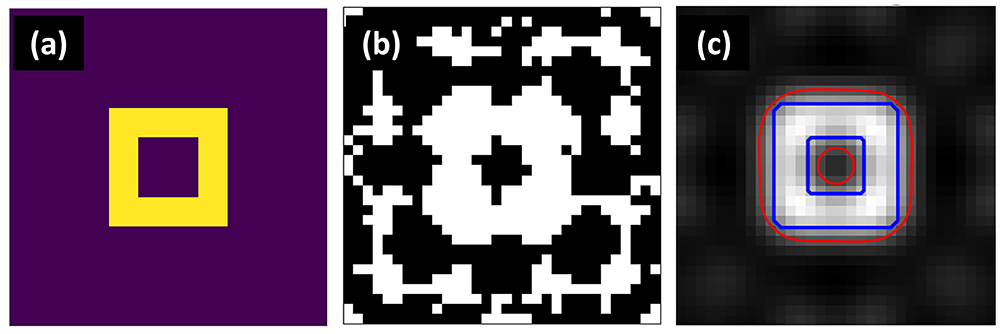
Exploratory inverse lithography technology (ILT) algorithm implemented using D-wave Hybrid Solver Sampler: (a) Target pattern on the wafer, (b) Optimized ILT mask pattern, (c) Aerial image, target contours (blue), and simulated contours (red) of the ILT mask.
-
Co-PI
-
Jhih Sheng Wu (National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University)
Inverse Reticle Optimization with Quantum Annealing and Hybrid Solvers
This project investigates the effectiveness of D-wave’s quantum annealer to address the complex and computationally intensive problem of photomask optimization in optical microlithography. By leveraging the adiabatic annealing theorem, the project aims to quickly and accurately calculate photomask designs that produce wafer images closely matching the target design. The significance of this technology lies in its demonstration of the potential and development of applying quantum annealing to the inverse optimization of photomasks. Combining quantum annealing with classical steepest descent algorithms significantly reduces execution time and improves optimization quality. The advancement of this technology can foster the integration of quantum computing with the semiconductor industry, greatly accelerating the application and development of quantum technology.
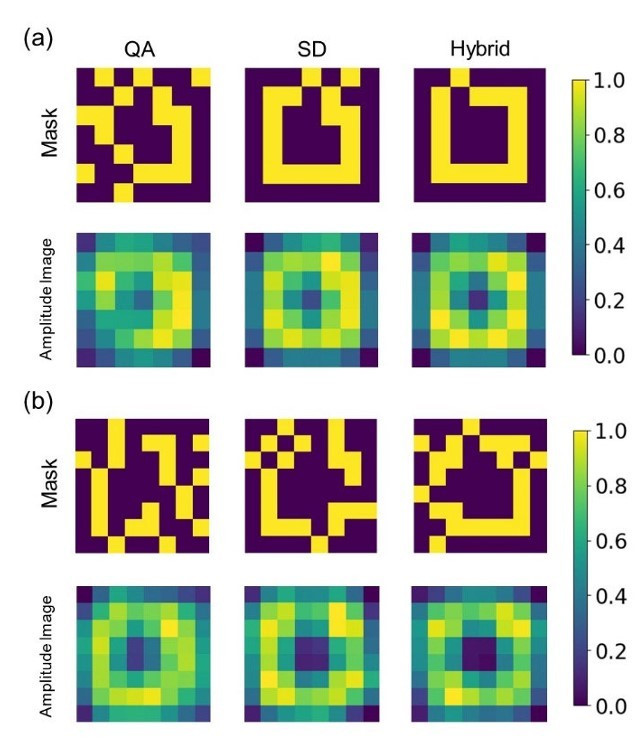
The optimal solutions of (a) 7×7 (b) 8×8 masks were calculated by Quantum Annealing (QA), Steepest Descent (SD), and hybrid QA+SD solvers with corresponding amplitude images.
Reference: Fang, P-H, Chen, Y-S, Wu, J-S, Yu, P (2024) Inverse reticle optimization with quantum annealing and hybrid solvers. IEEE Access 12:33069–33078
